WebAuthn / FIDO2 (YubiKey)
You can enable WebAuthn in the Ory Identity Service (Kratos) to allow users to perform 2FA with with physical devices such as USB keys or OS-level biometric authentication protocols, such as TouchID.
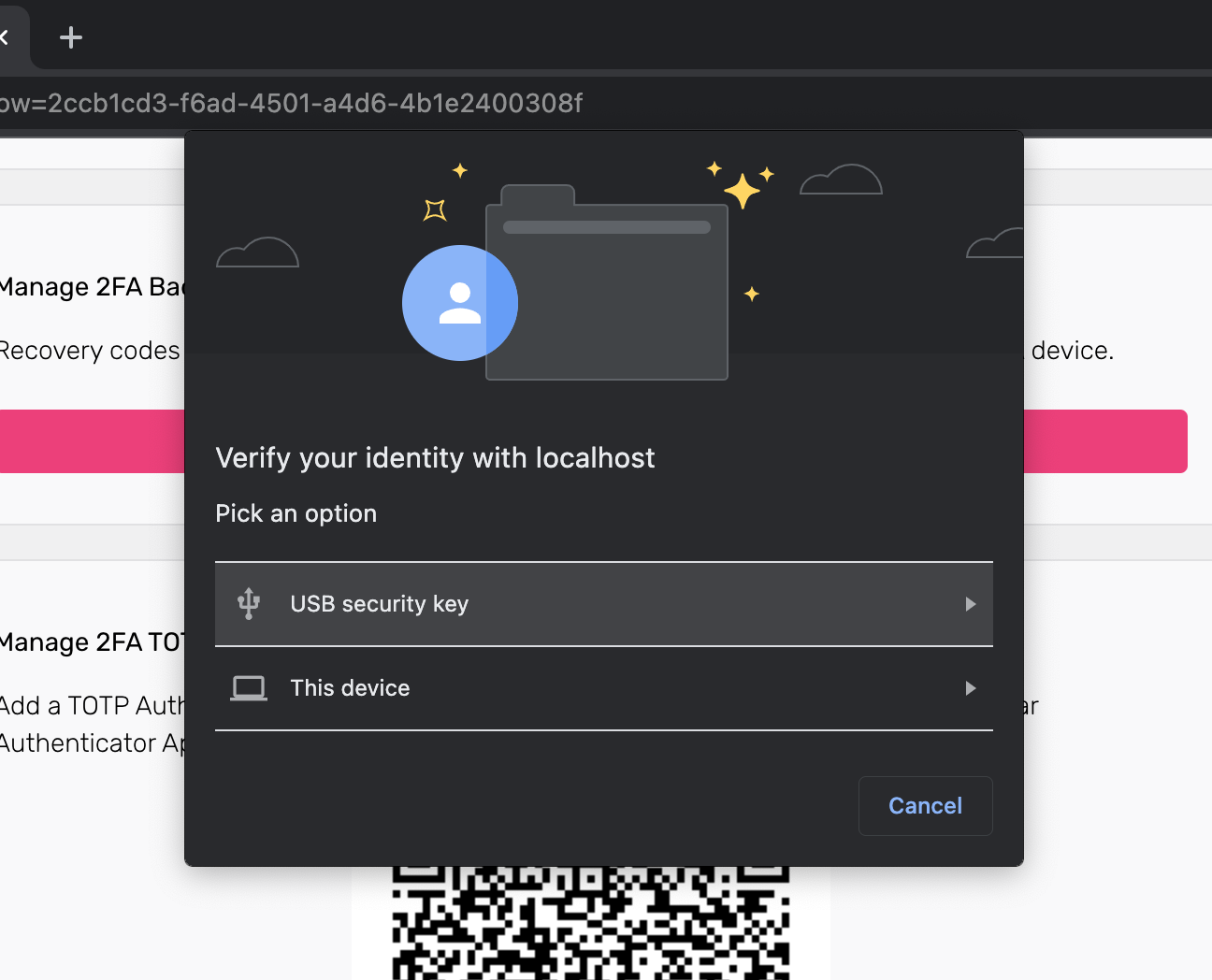
When users trigger the WebAuthn process, the web browser displays a prompt:
note
The look of the prompt depends on the web browser. The screenshot shows a Google Chrome prompt.
Constraints
- WebAuthn is a browser-only standard. It doesn't work with native mobile apps.
- WebAuthn is limited to one domain and does not work in a local environment when using CNAME / Ory Proxy. WebAuthN uses an
https://originURL as part of the client-server challenge/response mechanism. This mechanism allows a single URL as the origin. To learn more, read this WebAuthn discussion and on GitHub. - Depending on the framework you use, implementing WebAuthn in your own UI can be challenging. Check out the reference implementations to see how you can approach implementation for different app types (web app, SPA).
Configuration
Follow these steps to enable WebAuthn as the second authentication factor:
Ory Cloud Console
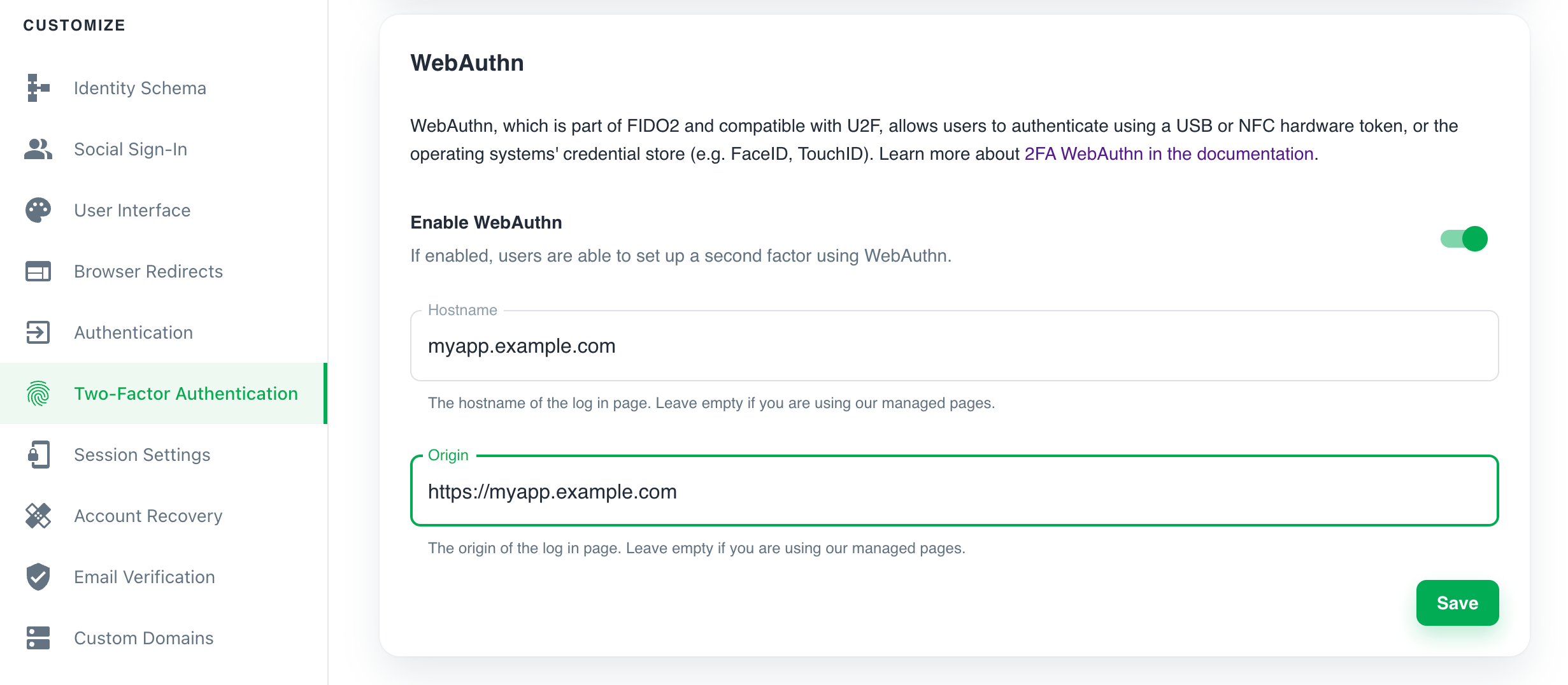
- Sign in to the Ory Cloud Console and go to Two-Factor Authentication.
- In the WebAuthn section, use the switch to enable WebAuthn.
- Define the hostname of your login page. You must set this to your top-level domain.
- Define the origin of your login page. Set it to the exact URL of the page that prompts the user to use WebAuthn. The relevant items are:
- scheme (http/https)
- host (
auth.example.com) - port (
4455)
note
If you are using the Ory Managed UI, leave these fields blank.
- Click Save to finish.
Ory CLI
- Get the Identity Service configuration from your project and save it to a file:
## List all available projects
ory list projects
## Get config
ory get identity-config <project-id> --format yaml > identity-config.yaml
- Find
webauthninselfservice/methods, setenabledtotrue, and define theid(hostname) andoriginof the login page users interact with:
webauthn:
config:
passwordless: false
rp:
display_name: MY_PROJECT_NAME
id: loginpage.com
# Set 'id' to the top-level domain.
origin: https://loginpage.auth.com:4455
# Set 'origin' to to the exact URL of the page that prompts user to use WebAuthn. You must include the scheme, host, and port.
enabled: true
info
The display_name is always set to the name of your project.
- Update the Ory Cloud Identity Service configuration using the file you worked with:
ory update identity-config <project-id> --file identity-config.yaml
Self-Hosted Instances
When working with self-hosted instances of the Ory Identity Service (Kratos), add the webauthn method to selfservice/methods
in the configuration file:
selfservice:
methods:
webauthn:
config:
passwordless: false
rp:
display_name: SAMPLE_NAME
# Set 'id' to the top-level domain.
id: loginpage.com
# Set 'origin' to the exact URL of the page that prompts the user to use WebAuthn. You must include the scheme, host, and port.
origin: https://loginpage.auth.com:4455
enabled: true
Distinguishing Identities Requesting WebAuthn
To help users distinguish which identity requests for WebAuthn authentication, add a webauthn object to the trait which
represents the WebAuthn account name.
In this example, the user's email address is the identifier:
note
This configuration is the default for all Ory Cloud projects.
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"traits": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"email": {
"type": "string",
"format": "email",
"title": "Your E-Mail",
"minLength": 3,
"ory.sh/kratos": {
"credentials": {
// ...
"webauthn": {
"identifier": true
}
}
// ...
}
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
}
}
Writing E2E Tests
When writing end-to-end (E2E) tests for WebAuthn implementation in your app, you can reference the Cypress tests used in Ory Identity Service (Kratos).
tip
To learn more about the approach used in Cypress, read this GitHub issue.